Supporting activities
Use the following iterative approach when executing a coordinated effort to inventory, document, prioritize, and analyze hundreds of processes (or more) by using the analysis techniques that are outlined in the preceding section.
- Identify and catalog all processes listed below No modeling or diagramming is required at this level. This initial cataloging of business process can be managed centrally and collaboratively (with a tool such as Blueworks Live), but primarily is done by process owners from their respective business units.
| Process | Examples |
|---|---|
| ID | 1, 50, FZ64A |
| Current format | Visio, PDF, Word, PowerPoint |
| Process name | Negotiate contract |
| Status | Current, Out of Date, Tribal Knowledge |
| Process owner | Owner’s name |
| Original author | Author’s name |
- Complete milestone level modeling in Blueworks Live for all processes and add another column named Process improvement tactic. This step too can be performed by process owners from their respective business units but governed by the BPM CoE for further discovery, analysis, and data collection.
|
Process |
Examples |
|
ID |
1, 50, FZ64A |
|
Current format |
Visio, PDF, Word, PowerPoint |
|
Process name |
Negotiate contract |
|
Status |
Current, Out of Date, Tribal Knowledge |
|
Process owner |
Owner’s name |
|
Original author |
Author’s name |
|
Process improvement tactic |
SOP, optimization, Blueworks Live Automation |
- Standardize all processes in Improvement Tactic categories that are related to BPM Automation or Swivel Chair. The process of standardization should involve modeling these processes down to the task level (but not to the action level).
- Perform Level 2 analysis on all processes that are identified in step (Steps 4 and 5 can be done in parallel.)
- Standardize all processes in Improvement Tactic categories other than BPM Automation or Swivel Chair. (Steps 4 and 5 can be done in parallel.)
Executive Sponsor
This role is the highest level executive who is sponsoring the entire BPM initiative (most likely, in the form of direct funding of the business case) in the organization that requires the BPM CoE.
- Provides senior sponsorship
- Leads direction-setting for the BPM CoE
- Establishes and evolves a funding model
- Governs the escalation processes
Business Architect
This role is typically a senior business and process engineering analyst who understand the entire value chain and was directly involved in creating the business case for the enterprise BPM initiative.
- Establishes and documents the enterprise value chain
- Initiates and governs the enterprise process inventory and analysis exercise
- Develops and prioritizes enterprise process road map
- Establishes and governs analysis standards
- Establishes and governs measurement standards
BPM Technical Architect
This role is the highest level of technical leadership involved in selecting and owning the BPM infrastructure (BPMS) in the organization. This person makes key strategic decisions involving, using, acquiring, and phasing out technology in the BPM software stack.
- Plans and evolves system capacity and architecture requirements
- Establishes an enterprise architecture stack involving the BPM system
- Creates, standardizes, and governs “best fit for purpose” guidelines for the BPM system
- Promotes and governs process and rule component reuse
- Articulates system performance and capacity management expectations to the shared infrastructure group
BPM Strategy Lead
This role is typically someone in a full-time project or program management role for the entire Center of Strategy. This lead acts to organize, articulate, and drive the agenda set by the other core members. This role is key because the other members likely do not have a full-time commitment to the BPM CoE strategic mission.
- Manages the strategic elements of the BPM CoE
- Prioritizes overall project pipeline
- Plans and prioritizes overall talent development requirements
- Establishes and governs delivery method standards
- Tracks execution across overall project portfolio
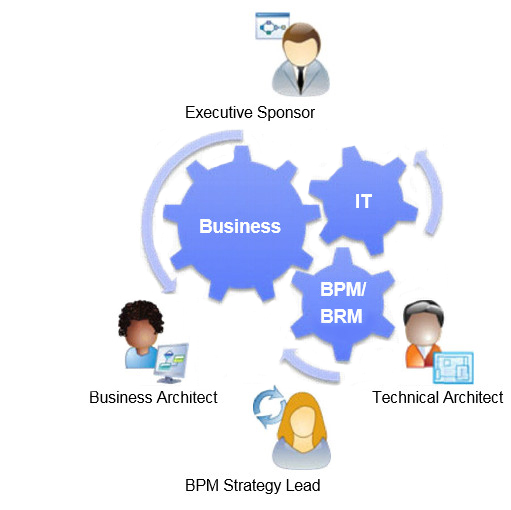
We suggest that at least one distinct person be assigned accountability for each role, and that individuals must have prior relevant delivery capability even if they are not assigned delivery responsibility.
