Error handling
If the platform support team must be contacted each time an application error occurs, the team might easily be overwhelmed. Therefore, an important approach is for process applications to do as much self-service error handling as possible. Errors should be properly caught at the service and process levels; processes can and do fail, which is universally recognized. By using a Process Administrator participant group in process diagrams can help to rectify top-level failures.
For example, system lane activities do not have a user interface, so errors usually cannot be caught and serviced within the services themselves. Therefore, catching exceptions at the BPD layer is important so that the process flow can be sent to application support personnel to handle and retry.
Often, the business will resist the concept of an Application Administrator. It might be a foreign concept to the business or it might be a topic that was not discussed during process discovery. As part of a process review, the question to be asked is “What happens if this activity fails?” A failed activity is a business problem and requires a business solution.
Organization in depth
The organization of the shared infrastructure element of a BPM CoE requires specific skills that are envisioned in roles, which are then organized in a decision-making and executable structure against the areas of responsibility of those roles.
Executive Sponsor
This role is for the highest-level executive who has responsibility for the shared infrastructure (most likely in the form of direct ownership).
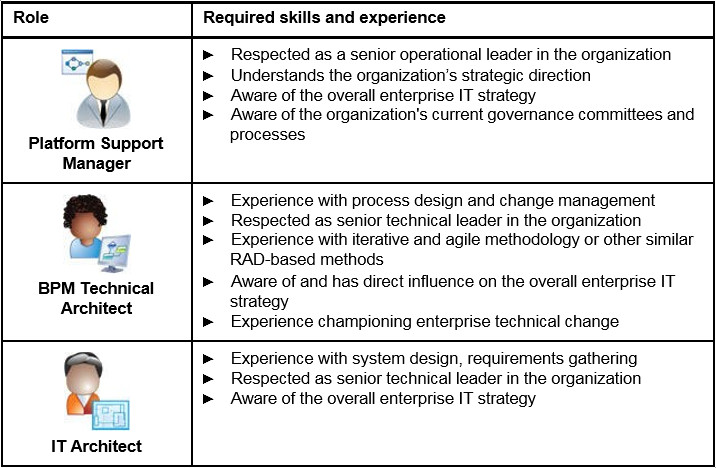
Platform Support Manager
This person is in charge of the platform support team that “owns” the BPM platform.
- Monitors system runtime performance.
- Provides Level 1 support for runtime environments.
- Works with application owners and application support teams to help resolve issues.
- Establishes common patterns and sets standards for application logging (business event versus system or technical logging) error handling, and process instance recovery.
- Ensures compliance with code promotion standards.
BPM Technical Architect
This person makes key decisions regarding the BPM software stack. The same person is also a member of the Center of Strategy.
- Plans and evolves system capacity and architecture requirements.
- Works with the IT Architect to develop best practices for integration into the enterprise architecture stack.
- Works with IT Architect to ensure all BPM touch points are secured.
- Establishes authentication and authorization standards for the BPM platform.
- Establishes common standards in regard to application logging, error handling, and recovery.
- Establishes platform topologies that provide appropriate scalability and availability.
- Establishes code promotion standards.
IT Architect
This role is a senior IT Architect who helps navigate through corporate compliance, topologies, and integrations.
- Ensures compliance with corporate IT standards and practices.
- Helps navigate through corporate IT governance bodies.
- Proposes appropriate integration technologies that incorporate existing corporate assets such as SOA, ESB, or data marts.
- Ensures usage of enterprise services in BPM solutions.
- Establishes overall security standards for intellectual property protection.
- Complies with corporate disaster recovery requirements.
Platform Administrator
This role has the following responsibilities:
- Ensures the integrity, security, and availability of the overall system.
- Creates new process applications, provision process applications, administer user authentication.
- Typically, this role is a full-time commitment from a member of the Platform Support team.
Network Administrator
This role has the following responsibilities:
- Offers specialized skills in the domain of the DMZ tier (“demilitarized zone”).
- Takes direction from the Platform Support Manager on overall requirements for the BPM solutions.
Database Administrator
This role has the following responsibilities:
- Implements and maintains the database tier that supports the BPM solutions.
- Takes direction from the Platform Support Manager on overall requirements for the BPM solutions.
BPM Support Engineer
This role understands the technical composition of the solution, and also the business problems it is intended to solve.